Business process automation has undeniably reached new heights in the last decade. In part this rapid pace of innovation has been made possible by Robotic Process Automation. The automation technology has seen massive adoption since traditional workflow automation was phased out. However, a new wave of digital transformation is already manifesting in the form of Intelligent Automation.
From software scripting to enable performance of rote tasks to introducing virtual assistants, or robots, — the automation journey has come a long way since the early 1990s, when Structured data interaction (SDT) was introduced. Yet, it was only in 2019 that Gartner included the Robotic Process Automation (RPA) category to its Magic Quadrant.
Digital transformation today relies on far more complex and interwoven technologies, some of which do not even require human involvement (but more on that later). Below is a look at some of the technologies that businesses can use to start on their Intelligent Automation journey, using attended and unattended automation.
Types of automation technologies
According to EY’s paper on IA, Global Business Service (GBS) rely on the following forms of automation technologies:
Structured data interaction (SDT) — a traditional automation technology that relies on the exchange of structured data between systems integrated through API’s or other tools to automate task execution. Relies heavily on human participation.
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) — a robotic software technology used to script well-defined and systematized activities, thus allowing to automate repetitive processes. Relies on robot-human interaction.
Machine Learning (ML) — an algorithm-driven technology that can make predictions or decisions based on assimilated data.
Natural Language Processing (NLP) — statistics and algorithm-backed technology that analyzes unstructured information to infer meaning, sentiment, and intent. Powered entirely by human-provided data.
Natural Language Generation (NLG) — a generative technology capable of producing structured information based on a dataset. Relies on pre-programmed or analyzed structures.
Chatbots and Virtual Agents — systems capable of interpreting text and/or voice in an unstructured format. Pre-programmed by humans, but capable of independent learning.
AI-Decision Systems — a number of technologies, models, and deep learning systems with cognitive capabilities to drive complex and inter-related decision making with little to no human participation.
What Intelligent Automation does integrally is combine RPA’s capabilities to perform tasks with Machine Learning capabilities. These can include automatic process mining, cognitive technologies (Computer Vision, Natural Language Processing, etc.) In other words, IA removes dependence on human involvement. However, before IA can be implemented across the board, there is more to be done with RPA.
What is Attended Automation
Often referred to as Attended Robotic Process Automation, attended automation is very simple in concept. It is a solution that helps complete business tasks through a collaborative approach of human and robotic work.
Attended automation solutions have been used for both back-end and front-end operations. A vivid example of this are call centers and service desks, wherein the robot automates a portion of the tasks before passing the work for review or further processing to a human worker. This is also known as task-based automation.
While previous types of technologies helped automate back-end tasks, attended RPA has allowed to leverage integrations between systems. Much like a human worker, a virtual assistant still interacts with a virtual workstation, an electronic interpretation of a desktop computer’s controls, which can interact with databases and integrated systems.
However, according to SSON’s study, 42% of companies rely on unattended automation, compared to 27%, who rely on attended solutions.
Unattended Automation
Sometimes referred to as Robotic process automation 2.0, unattended automation, as you can infer from its counterpart’s definition, does not imply human involvement. At least not entirely.
Unattended automation will utilize any of several implementations of Cognitive and AI technologies. In practice, this means the technology can perform process mining and process mapping on its own in order to discover best process efficiencies. It also works with unstructured data and relies on prior data analysis in order to make conclusions and predictions as to how the process ought to work.
The word process cropped up more than once in the last paragraph and that was intended, as implementing unattended automation usually means transitioning from task-based automation to processes-based automation.
Its benefit over attended RPA is that it not only raises productivity, but that it can do so at scale, significantly speeding up processes and allowing the human workforce to focus on high-level, value-driving work.
Perhaps most interesting is that attended automation drives unattended automation. When machine learning and cognitive capabilities are connected to attended solutions, they can utilize the data generated by human-robot collaboration for capacity building. Simply put, attended automation is the key to unlocking the path to Intelligent Automation.
Attended vs Unattended RPA
Having looked at the two Intelligent Automation technologies separately, let’s compare Attended and Unattended Robotic Process Automation side by side. This will paint a clearer picture on the advantages and disadvantages of Attended and Unattended RPA and point as to the scenarios both can be used.
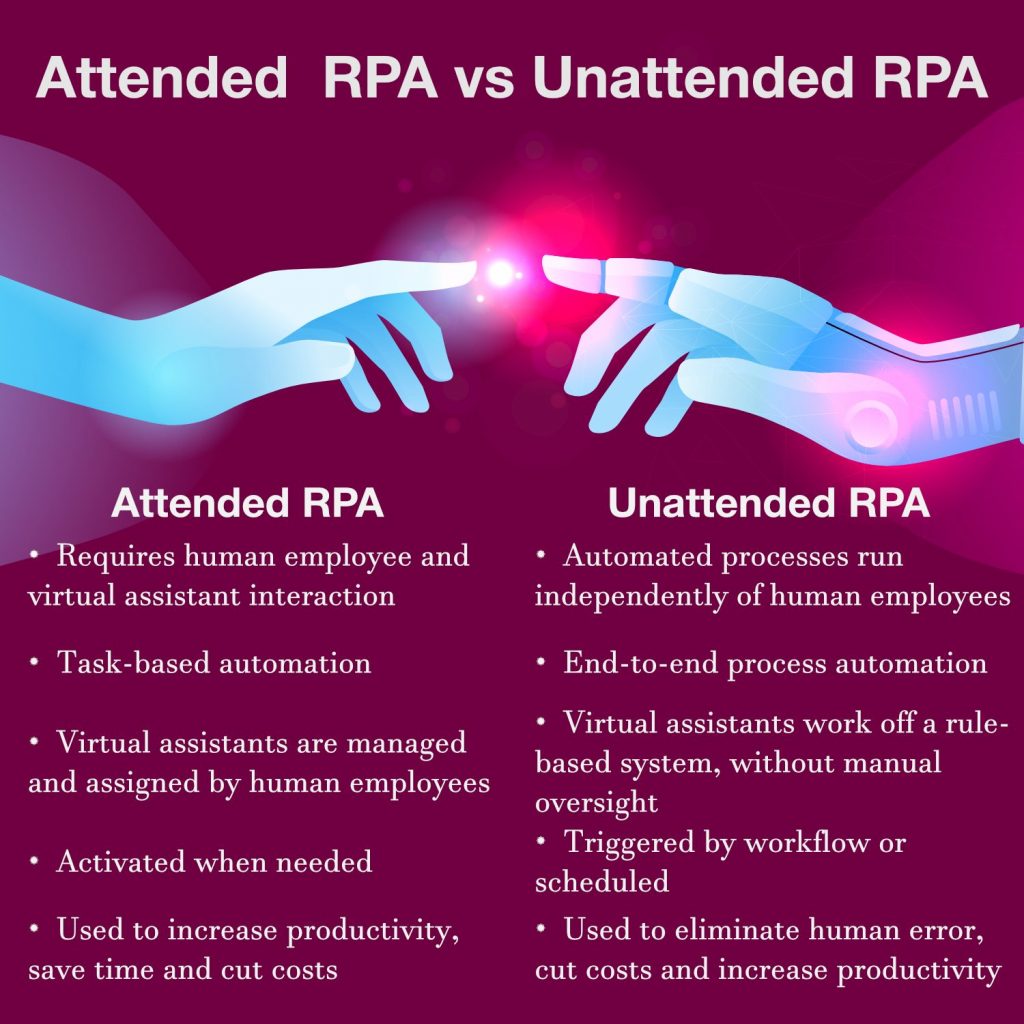
As evident from the table above, business processes can benefit from Attended RPA if they run menial processes that involve dealing with large volumes of data. By removing human-error and letting the human be in charge of decision making, rather than manual analysis, automated automation creates the perfect human-bot cooperation.
On the other hand, Unattended RPA removes the human from the process altogether, surrendering the heavy data lifting and repetitive work to virtual assistants.
Impact of RPA on the workplace
The benefits of task and process automation are innumerable. Apart from releasing human staff from mundane work to allow them to focus on those requiring interpersonal or highly specific skills. Many claim that automation helps enhance human intelligence in ways that allow people to make informed decisions and have future-ready solutions.
However, to begin the automation journey, business leaders will need to facilitate the adoption with actual people. Because automation requires a seamless integration of processes, people and technology, they will need to prepare, upskill, and familiarize the workforce for what is to come. Despite negative sentiment overall, concerning the replacement of humans, knowledge workers are prepared to welcome it and believe it will enhance operations, according to the Shared Services report from SSON.
Organizations and businesses that are ready to embrace Intelligent Automation can look forward to providing an error free and exceptional customer service, more time on high-level tasks by human employees, and organized, actionable data in the moment.
How it could work
EY claims that for maximum value, both the business and IT teams will need to collaborate in order to make the most of RPA. The way to making IA work is through an integrated business-technology approach.
By relying on Global Business Service partners, business process outsourcing providers or by building a dedicated development center, businesses will be able to transform the back-office into a digital innovation hub. Moreover, by re-evaluating their hiring methodology, businesses can support the technology-first approach, by hiring or re-skilling existing employees to assure computer-literacy at the required levels.
To discover how you can begin the Intelligent Automation journey and how it could work for your business, consult your strategic technology partner. You can also discover examples of how it has already worked through SSON’s database of vendors and IA implementation case studies.
24 April 2020

 Pavel Kaplunou
,
Pavel Kaplunou
, 



